Evolution of Costing Systems:-
American academicians and practitioners tried to understand the techniques and methodologies used by Japanese Multinational companies and started publishing papers of the same. Target Costing (genka kikaku), Kaizen, Kanban, 5S and others emerged from these studies.The first was primarily related to costs and the rest is meant for improved productivity, quality, and efficiency techniques. Parallelly due to the emergence of Maruti Suzuki as No. 1 car manufacturer in India, these techniques were adopted by most of the auto component suppliers as the same was insisted upon by the end customer. All these techniques are exceptionally good practices which can be adopted without any reservations across the spectrum of small to large entities. At the same time, it was a shock that Japanese did not practice any full-fledged costing system which could be easily adopted by the Indian companies. It was a revelation that they understood the logic that past is history which cannot be corrected and the best method of costing is that which can compute the cost, before even the first step is taken to manufacture the product.They also understood that cost can be optimized only through processes, quality, and best housekeeping at the shop floor level. At best cost variances may have to be analyzed more from the nonmonetary parameters and that too on a shift wise basis wherever possible. This way “Poka Yoke” (Error Proofing) became equally applicable to Costing under the Japanese techniques. Moreover, the above Japanese techniques are mostly meant for Engineers and other skilled technicians who control the costs on the go, even on a shift wise basis, with little room for our members as well as our counterparts in USA, UK, and other countries.The main problem of the costing profession across the world is on concentration of the past rather than the present and future.One of the authors of the above book “Relevance Lost” Prof Robert Kaplan made further research at Harvard University and came out with an alternative method for allocating overheads using “activities” instead of conventional methods and probably it is one way of addressing the deficiencies of the conventional costing systems. The other author Prof Johnson did notsubscribe to his co-author’s views and published a book namely “Profit Beyond Measure” in the year 2020. In this book he analyzed two international auto companies Toyota of Japan and Scania of Sweden for their best profit performance for a continuous period of five decades. Incidentally both these companies were from non-English speaking world and author did not give much of details of the best practices these companieswere adopting in their costing systems for consistently making profits.
What is GPK:-
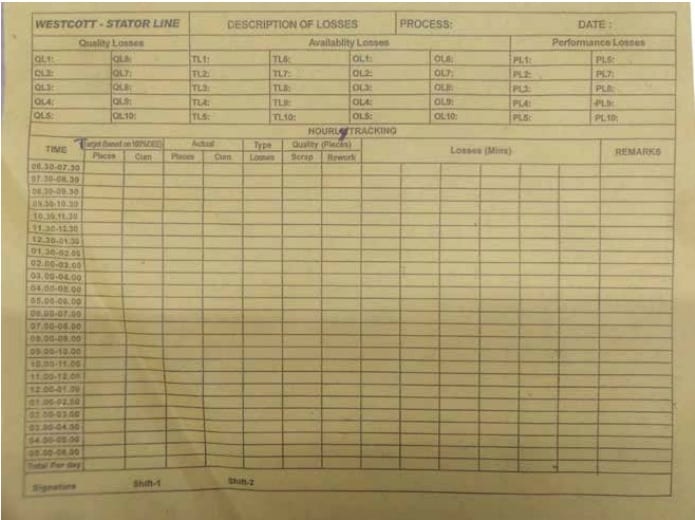
The above made the author of this article to search for best full-fledged costing practices adopted in the nonEnglish speaking countries but language barrier made the job difficult. Incidentally,an opportunity emerged through one of the German customersto interact closely on internal practices involving quality, productivity, performance, and cost. A simple sheet of paper “Hourly monitoring sheet” was the sparking point to get glimpses of German Costing practices. Copy of a “Hourly Monitoring sheet” is enclosed but what is used in inside the factory is in local language where the field level operator can understand and fill the same on his own. American Universities as well as our counterpart “Institute of Management Accountants” USA also published articles on German Costing systems from the year 2000 onwards. They also tried to implement the same in the American companies and used the jargon “Resource Consumption accounting” for the same. However, the undersigned found out that German customer was using just a modified “standard costing”routinely where the standards are derived from engineering and not the conventional terms used by the Cost Accounting profession. Along with the academic learning from some of the translated articles from German publications it was possible to find out that GPK is nothing but a combination of Marginal Costing and Standard Costing. We are well versed with material accounting which we are using in many of our companies right now and the same is used by Germans also. Hence there is no change in the methodology as compared to our present practices of material accounting and only difference is, they are using “Standard Costing” rates for material issues instead of weighted average, FIFO, LIFO, and others.
More about GPK:-
Now let us analyze other items of manufacturing such as labour, power, machine, other items (tools, dies, jigs &fixtures), floor space, power consumption and other utilities. The hourly monitoring sheet captures all these items in a systematic manner and using standard costing principles costs could be assigned to products and services on a perpetual basis. ISO standards emerged from Europe only and the same could be used for most of the information required for setting standards of individual components. ISO also issues global benchmarks and averages of utilization of various inputs such as labour, machines and others which could be used for setting internal standards through discussions with internal cross functional teams. It can be pointed out that all the standards referred to ISO etc. are all engineering, quality and process standards. In Standard costing we use two variable components for each item.One will be invariably non- financial and the other being financial. For example, if we take Material, price is financial, and usage is non-financial. Similarly, inLabour rate is financial and efficiency is non-financial. The non financial information could be gathered from the records of ISO or any of the standards being followed by entities. Although in this article manufacturing entity are referred mostly, they are equally applicable to service sector also. In service sector specially in the IT field the log in and log out requirements enable auto collection of key information and populating the same with an online cost system. The SOPs also enable strict implementation of the system without any room for deviation. When the labour, machine, electricity and other resources are measured through Hourly Monitoring Sheets, the same could be linked with relevant standard costs to arrive at product costs in a logical manner. Based on the variance analysis done after the closing of the month, standards could be revised through discussions with the same internal cross functional teams.If variances are within tolerable limits, there is no need to revise the same on regular basis. Even higher executives could be advised to record their usage of time on daily basis on each product and service so that the same could be incorporated in product costs. The author of this article earnestly feel that almost 90% of the costs could be linked to product/service costs. When we can logically link majority of these costs with products and service, contribution approach in the marginal costing principles could be straight away used for price fixing and other decisions with respect to products and services.
Why GPK is a Robust System:-
Since the GPK was developed by an automobile engineer late Mr. Plaut and an academicianlate Mr. Kilger it was made robust meeting both actual real time practice as well as academic validations. At the same time,it was designed right from the beginning in a highly flexible manner so that adoption across different sizes of the organization as well as multiple sectors made easy. Recording “Time related Costs” was the biggest challenge in the costing systems and Germans mastered the same over past several decades. Popular ERP system “SAP” is a German product and these techniques are in built in the same and are being used by several leading German companies including Daimler Benz, Volkswagen, BMW, Siemens, Bosch, Deutsche Bank, Deutsche Post and others for several decades. Since the system is highly flexible many small and medium enterprises in German speaking countries such as Germany, Switzerland and Austria are using the same for several decades and also perfected it over this period.
Control through GPK:-
Since Standard Costing is used right from micro level, fixing responsibility, and improving performance from lowest to highest levels is made possible. “Cost Management” is the main objective of GPK and inventory valuation is just a bye product restricted to financial statements only . Even in inventory valuation of work in process, standard costs could be assigned to each process level completion of jobs and the valuation could be determined more accurately. The system also enables us measure idle time of man, machine and other resources and the concerned division heads could be made responsible for wasting the precious resources of the organization. In effect the system fully supports performance management . Rejection, rework, wastage, and spoilage are all recorded perpetually at each individual process level and the concerned manager could be made responsible for the losses. Productivity improvements are possible using the system and the same operator manages two or three processes simultaneously as the time taken for loading a component into a process is much less than the time taken by the machine to complete the process.
Conclusion:-
In conclusion, the system is the need of the hour in our country as well as for our members to focus performance improvement of the organization. Our members have learnt Standard Costing during their academics, and they must unlearn what they have learnt and relearn the same from an engineering perspective for actual implementation at the field level. Most of our members uses Marginal Costing regularly in their organizations and they should now combine the same with standard costing techniques not only for score keeping but also for overall performance management. Recommended
Sub Fields of AccountingProfit CentreClassification of Various CostsProfit CentreBackorderCA Final Result