The long-awaited GST regime is all set to roll out with the President assent to the following four GST related Bills :
Central GST Bill, 2017The Integrated GST Bill, 2017Union Territory GST Bill, 2017GST (Compensation to States) Bill, 2017
The law will replace various indirect taxes with one simple tax, creating a boundary less and a unified national market that will also lead to increase in country’s GDP. Implementation of GST would bring many professionals opportunities for Company Secretaries in Practice and employment in terms of compliance, advisory, tax planning, etc The comprehensive tax structure passed through various stages before being implemented
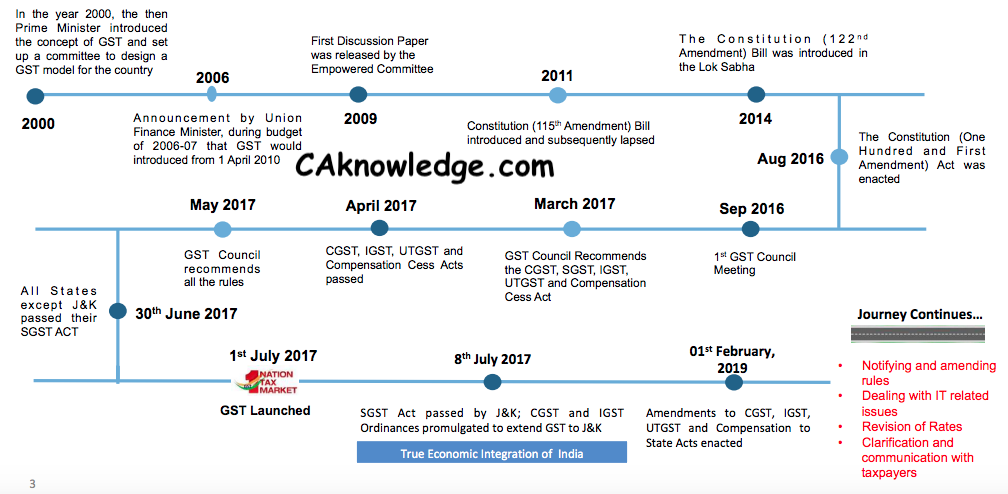
History of GST, Historical Background of GST
The origin of Goods and Services Tax could be traced back to July 17, 2000, when the Government of India set up the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers with the Hon’ble State Finance Ministers of West Bengal, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Delhi and Meghalaya as members with the following objectives:
to monitor the implementation of uniform floor rates of sales tax by States and Union Territories;to monitor the phasing out of the sales-tax based incentive schemes;to decide milestones and methods of States to switch over to VAT; andto monitor reforms in the Central Sales Tax system existing in the country.
History of GST
GST Law from a Constitutional Perspective
Definition of GST – “Goods and services tax” means any tax on supply of goods, or services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption “Goods and Services tax” law while having unique principles, has significant elements of prior Central and State laws; and is also inspired by VAT/GST legislation of EU, Australia, Malaysia etc. along with International VAT/GST guidelines of OECD Bill passed by Rajya Sabha on 03.08.2016 & Lok Sabha on 08.08.2016 Notified as Constitution (101st Amendment ) Act, 2016 on 08.09.2016 Key Features:
Concurrent jurisdiction for levy & collection of GST by the Centre & the States – Article 246ACentre to levy & collect IGST on supplies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce including imports – Article 269ACompensation for loss of revenue to States for five years on recommendation of GSTC – Clause 19GST on petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas & aviation turbine fuel to be levied from a later date on recommendations of GSTC
Status of GST Law 2017
The following laws have been passed by the Parliament followed by President’s assent : The 14th meeting of GST Council shall be held on 18-19 May, 2017 to finalize the fitment of commodities in the four- tier rate structure and to finalise draft rules. CBEC has issued total 11 GST rules as follows, which are available in the public domain on CBEC website :
(i) GST Composition Rules(ii) GST Valuation Rules(iii) GST Transition Rules (iv) GST ITC Rules(v) GST Revised Invoice Rules (vi) GST Revised Payment Rules(vii) GST Revised Refund Rules(viii) GST Revised Registration Rules(ix) GST Revised Return Rules(x) GST Assessment and Audit Rules(xi) GST Electronic Way Bill Rules
Recommended Articles
Key Definitions Under GSTGST Overview With ExampleTax Structure of GSTWhen will GST be applicableWhy GST For IndiaGST ReturnGST RatesGST Registration
If you have any query or suggestion regarding “History of GST, Historical Background of GST” then please tell us via below comment box…