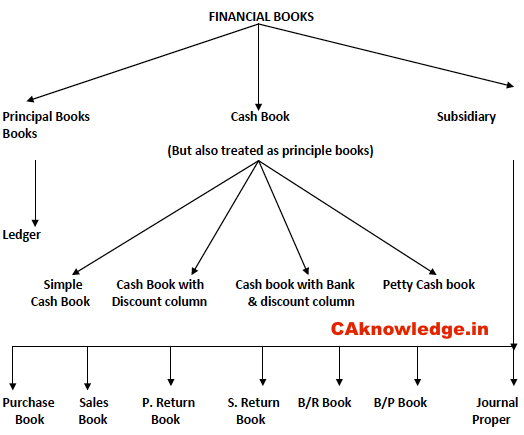
The system by which transactions of a class are first recorded in the book, specially meant for it and on the basis of which ledger accounts are then prepared is known as the Practical System of Book keeping or even the English System. It should be noted that in this system, there is no departure from the rules of the double entry system
Subsidiary Books – Introduction
These books of original or prime entry are also called subsidiary books since ledger accounts are prepared on their basis and, without the further process of ledger posting, a trial balance cannot be taken out. Normally, the following subsidiary books are used in a business: (i) Cash book to record receipts and payments of cash, including receipts into and payments out of the bank. (ii) Purchases book to record credit purchases of goods dealt in or of the materials and stores required in the factory. (iii) Purchase Returns Books to record the returns of goods and materials previously purchased. (iv) Sales Book to record the sales of the goods dealt in by the firm. (v) Sale Returns Book to record the returns made by the customers. (vi) Bills receivable books to record the receipts of promissory notes or hundies from various parties. (vii) Bills Payable Book to record the issue of the promissory notes or hundies to other parties. (viii) Journal (proper) to record the transactions which cannot be recorded in any of the seven books mentioned above It may be noted that in all the above cases the word “Journal” may be used for the word “book”
Advantages of Subsidiary Books
The use of subsidiary books affords the undermentioned advantages : (i) Division of work : Since in the place of one journal there will be so many subsidiary books, the accounting work may be divided amongst a number of clerks. (ii) Specialisation and efficiency : When the same work is allotted to a particular person over a period of time, he acquires full knowledge of it and becomes efficient in handling it. Thus the accounting work will be done efficiently. (iii) Saving of the time : Various accounting processes can be undertaken simultaneously because of the use of a number of books. This will lead to the work being completed quickly. (iv) Availability of informations : Since a separate register or book is kept for each class of transactions, the information relating to each transactions will be available at one place. (v) Facility in checking: When the trial balance does not agree, the location of the error or errors is facilitated by the existence of separate books. Even the commission of errors and frauds will be checked by the use of various subsidiary books. Recommended Articles
Accrued LiabilitiesAccounting Standard 15: Accounting for Retirement BenefitsList of Ind AS Notified by MCAAccounting for Rectification of ErrorsDistinguish Accounting, Auditing and InvestigationMeaning of Accounting & Scope of AccountingVarious Types of Vouchers In AccountingTips for Avoiding Personal Finance Mistakes